How to Grow Lupine: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
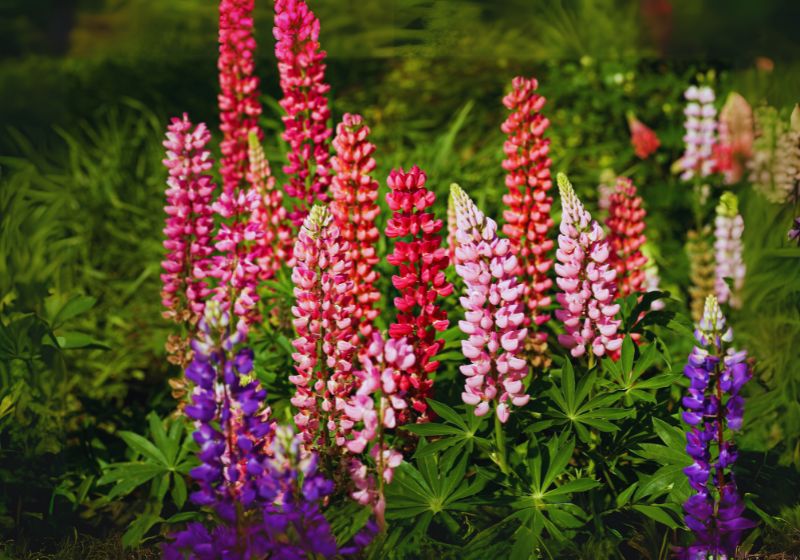

The garden landscape looks stunning with lupines because these perennial and annual flowers bring vibrant plant colors. The tall spiny blooms of these flowers grow along with deep green foliage and the plants have both low maintenance requirements and a strong attraction for bees and butterflies. All information needed for achieving lupines garden success is comprehensively presented in this guide.
Understanding Lupines
- Slavonia Epacris and Savage Valley Epacris form two out of the more than 200 species within the Lupinus genus.
- As a genus with 200 species these plants exist in blue, purple, pink, yellow and white color variations. Two varieties of lupines plants which gardeners mostly cultivate include.
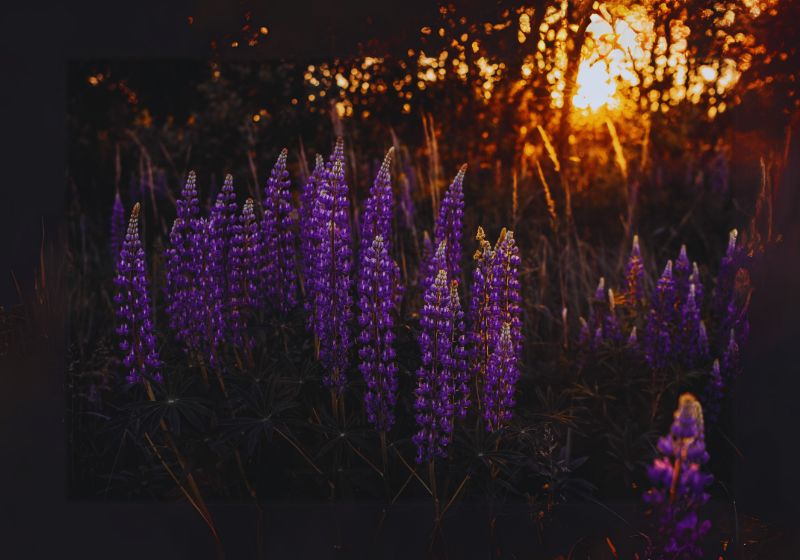

- The perennial Lupines (Lupinus polyphylies) survive from year to year in cool climate regions.
- The annual species Lupinus luteus and Lupinus metabolism create blossoms annually before seeding themselves to reproduce in upcoming years.
- These plants require a climate with cool weather while they need to grow in well-drained slightly acidic soil conditions. Understanding how lupines require care will lead to successful plant growth.
Choosing the Right Variety
You should choose from these preferred lupine types when designing your garden flower beds:
- Russell Hybrid Lupines : Known for their tall, colorful spikes and adaptability.
- Texas Bluebonnet (Lupinus teensiest) :stands as the official flower of Texas because it displays attractive blue and white petals.
- Arctic Lupines (Lupinus arcticus) :demonstrates exceptional hardiness as well as resistance which makes it a good choice for cold areas.
- Bigleaf Lupines (Lupinus polyphylies) :shows its strength through its many dense flower spikes while growing robust perennially as a plant.
- Select your lupines :variety by considering both your geographical climate and garden appearance preferences.
Preparing the Soil
- Group lupines succeed in drainage-friendly soils that maintain a pH reading between 5.5 to 7.5.
- The following process describes the correct methods for soil preparation:
- The Soil pH level requires evaluation through a soil test kit.

- Sulfur and peat moss should be applied to alkaline ground for pH reduction.
- You should mix either sand with organic compost to create better soil drainage.
- Loosen the Soil Lupines develop long taproots, so loosen the soil to at least 12 inches deep.
Planting Lupines Seeds
- Aphids are tiny insects which feed on plant fluids through sucking. Insecticidal soap or a water spray removes the pests from the plants.
- It is most effective to grow lupines through seed planting. To achieve successful germination maintain the following procedures.
- Lupines seeds need scarification since their coats remain thick. Wet seeds in warm water for one night and then sandpaper them slightly before putting them into the ground.
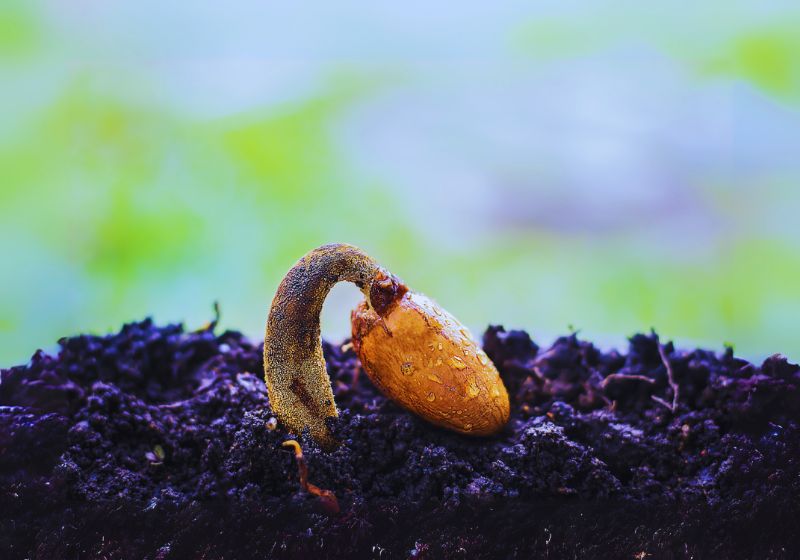

- Seeds should be directly sown during the early spring season or the fall period.
- Plants should be placed at ¼ inch depth with 12-18 inches of space between each seed.
- Maintain soil moisture between damp and saturated during the germination period which takes twelve to fourteen days.
- When planting seeds inside perform this operation four to six weeks before the final frost date until the seedlings develop sufficient strength for outside transplanting.
Caring for Lupine Plant
Watering

Lupines need moderate watering. To maintain proper soil moisture level plant owners should supply deep water once per week. The soil should stay moist yet avoid feeling soggy. Wetting the soil too much leads to root rot development.
Fertilizing

The lupines plant does not need strong fertilization to thrive. The capacity of lupines to extract nitrogen from the soil leads to many leaves instead of blossoms when given excessive nitrogen. Users can fertilize their lupine plants in early spring by applying a balanced fertilizer with low nitrogen content (equivalent to 5-10-10).
Mulching

Organic wood chips or straw mulch put around lupines plants provides essential moisture retention as well as weed suppression combined with temperature regulation of the soil.
Pruning and Deadheading

- Deadheading spent flowers will stimulate further blooming on these plants.
- After the flowering season plants should have their foliage trimmed for better plant health across the following growing period.
Common Pests and Diseases
- Lupines present moderate resistance against pests but some specific problems which include:
- The soil should stay moist yet avoid feeling soggy. Wetting the soil too much leads to root rot development.
Pests
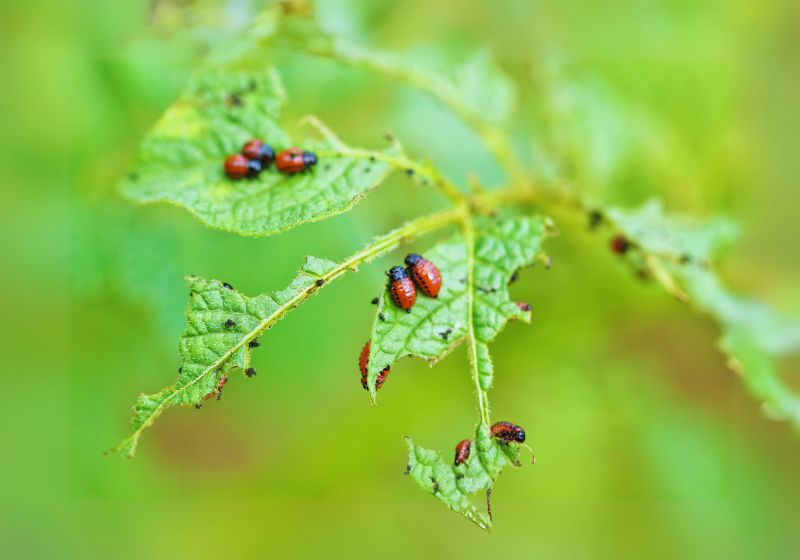

- Aphids are tiny insects which feed on plant fluids through sucking. Insecticidal soap or a water spray removes the pests from the plants.
- The garden faces two major problems as slugs along with snails consume leaf tissues. Crushed eggshells together with diatomaceous earth will keep these pests away.
- To control severe caterpillar infestations you should either handpick the caterpillars or treat the plants with organic pesticides.
Diseases

- Powdery Mildew : Appears as white powder on leaves. The prevention of diseases includes using fungicides along with proper ventilation in the growing area.
- The excessive supply of water creates the condition known as Root Rot. The soil should drain properly to prevent disease formation
- Fungal Leaf Spots : Prune infected leaves and avoid overhead watering.
Propagation Methods
Seeds

- This guide provides beginners with everything needed to successfully grow lupines which will produce gorgeous blooms every year.
- Harvest seeds from dry plant pods in late summer.
- The seeds need to stay in a dry and cool environment before the planting period starts.
Cuttings

- Use healthy plant materials to take basal cuttings in the early part of spring.
- Put the cut end into rooting hormone before placing it into moist soil.
Division

- The perennial lupines need dividing only every 3-4 years at the beginning of spring.
- After carefully extracting the whole root system you should replant various sections which contain healthy root structures.
Companion Planting
- Plants that grow lupines serve two purposes: they improve soil fertility by performing nitrogen fixation. They pair well with:
- The soil under rose: bushes benefits from lupines presence because these highly demanding plants extract nutrients from the soil.
- Daisies and Poppies : These flowers complement lupines blooms.
- Peonies and Irises : Create a vibrant, colorful garden bed.
- Plants of lupines should be kept away from resource-competitive spreading plants for optimal growth.
Overwintering Lupines
- The survival of perennial lupines in cold regions depends on obtaining winter protection measures.
- Cutaway plant leaves after the initial fall frost date arrives.
- A thick layer of protective mulch should be distributed around the base of the plant to provide insulation.
- Excess moisture during winter should be avoided to prevent root rot in lupines.
Harvesting Lupine Seeds

- There are two steps to harvest seeds for future plantings:
- Seed pods on the plant will naturally desiccate until they become brown and hard.
- Reap the pods when they show brown and brittle colors before the plant opens them.
- Keep seeds inside an airtight container which you should store at a cool and dry location.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Leggy Growth: Caused by insufficient sunlight. Ensure plants receive full sun.
- Yellow foliage stands for either drained soil or excessive water levels.
- Plants do not bloom when there are deficient blooms because of nitrogen excess or inadequate sun exposure.
- Plants of the lupines species grow optimally when planted in draining soil under sun or semi-shaded conditions and they need little maintenance after gaining establishment.
Stunning Aesthetic Appeal
Tall spikes of pea-like lupines flowers display aesthetic beauty through multiple colors from purple to blue and pink to red and yellow as well as white petals.
Pollinator-Friendly

The plant draws bees, butterflies and hummingbirds to its flowers which serves as an ideal option for gardens promoting pollinators.
- Reap the pods when they show brown and brittle colors before the plant opens them.
- Keep seeds inside an airtight container which you should store at a cool and dry location.
Nitrogen Fixation

- Producers of nitrogen from atmospheric gases and members of the legume family lupines enhance soil health which benefits nearby plants.
- Tall spikes of pea-like lupine flowers display aesthetic beauty through multiple colors from purple to blue and pink to red and yellow as well as white petals.
Low Maintenance

Plants of the lupine species grow optimally when planted in draining soil under sun or semi-shaded conditions and they need little maintenance after gaining establishment.
Deer and Rabbit Resistant

Dark bitter leaves of lupines along with alkaloids make deer and rabbits avoid the plants which protect your garden from their damage.
Erosion Control

The deep-rooted lupines function as soil stabilizers which makes them suitable for slope protection and preventing erosion within loose soil regions.
Versatile Landscaping Use

Hazards at garden beds and borders and wildflower meadows and pot containers give lupines the capability to enhance landscape design flexibility.
Conclusion
By planting lupines you acquire flowers with an added benefit of better soil conditions. When you provide careful maintenance these plants succeed in growing repeatedly to decorate your garden with lively beauty.
Hazards at garden beds and borders and wildflower meadows and pot containers give lupines the capability to enhance landscape design flexibility.
This guide provides beginners with everything needed to successfully grow lupines which will produce gorgeous blooms every year.
READ MORE : How to Grow a Crabapple Tree: A Comprehensive Guide

 English
English